- May 9, 2025
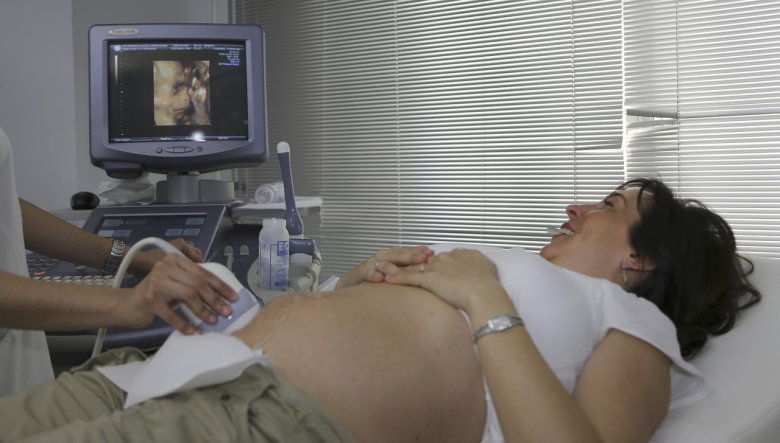
This is a simple and quick examination allowing doctors to detect many ailments. Ultrasonography is non-invasive and can be repeated at short intervals. What exactly is it all about?
USG in disease prevention
This is one of the basic diagnostic methods, thanks to which the leading doctor is able to determine what treatment to take and whether the current therapy has brought the desired results. The examination provides an insight into our organs, on a special screen you can see the size and shape of the liver, pancreas or ovaries. Allows you to quickly detect possible nodules before they give real symptoms. Thanks to ultrasonography it is possible to quickly detect a possible cancer, so that the patient has a much better chance of a cure. It is also a test commonly used during pregnancy, the doctor constantly monitors whether the fetus is developing properly, and can also determine the sex of the child. Ultrasonography is also very helpful during biopsy, allowing for safe tissue removal for more accurate examination.
How does ultrasound work?
Ultrasonography consists in the painless introduction of acoustic waves of very high frequency - from 1 to 10 Mhz - into the patient's body. The human ear is not able to catch them. They are completely harmless to the body, they do not destroy the cells, so that the result is readable, there is no need to introduce contrasting fluids. Waves hitting a given organ, reflect from it, then the acoustic impulse is turned into an electric one. This creates an image that is visible on a special screen. Individual organs reflect ultrasound in a different way, so it is easier to distinguish between them.
The section of the patient's body to be examined is lubricated with gel, which makes it easier to guide the head. The doctor gently moves the device on the skin, during which time the waves reach the organs and transform into an image. Acoustic waves are not able to penetrate the bone tissue, therefore brain ultrasonography is not possible, it is also impossible to determine the condition of the bone.